[Algorithm](EN) Hash table implementation in C/C++
Implement hash table in C/C++
Environment and Prerequisite
- C++
- Understanding of hash function and linked list
Hash Function
What is Hash Function?
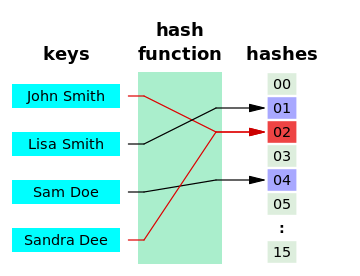
Hash Function: Hash function is any function that can be used to map data of arbitrary size onto data of a fixed size. Sometimes hash function result could be same. In this case we call this as Collision.(H(s1) = H(s2))- In below picture, blue things on left are keys and each key goes into hash function and result into right side hashe values. Later on in hash table values on right side will be used as hash table array index.
- Consider
H()as hash function, thenH(Jonh Smith) = 02
Hash Collision
- Case which different key results in same hash value.
- Consider
H()as hash function ands1ands2as different string, thenH(s1) = H(s2) - Solution for collision:
ChainingorOpen Addressing
Example
- Below sample is simple hash function which get string and return integer value;
- On internet there are many hash function implementations. Shift operation and prime number is widely used in hash function.
int hash(const char * str) {
int hash = 401;
int c;
while (*str != '\0') {
hash = ((hash << 4) + (int)(*str)) % MAX_TABLE;
str++;
}
return hash % MAX_TABLE;
}
Hash Table
- Data structure which save pair data
keyandvalue - Like below usage, it is a data structure use
Lisa Smithaskeyand save521-8976asvalue. - There are already hash table implementations in each language like map in C++ and dictionary in python.
- Theoretically, accessing time complexity is
O(c). Hash table use more memory but take advantage of accessing time. - Use
ChainingorOpen Addressingfor collision

Implementation
- In this post, I use
Chainingfor collision. - Use
Singly Linked ListforChaining
Common
- Hash table implementation using linked list
Nodeis for data with key and value
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#define MAX_TABLE 5 // size of table
#define MAX_KEY 8 // include null
#define MAX_DATA 12 // num of datas for hash table
#define DELETE_COUNT 6 // num of datas for deletion
#define FIND_COUNT 8 // num of datas for finding
struct Node {
char key[MAX_KEY];
int value;
Node * next;
};
Node * tb[MAX_TABLE]; // hash table
char keys[MAX_DATA][MAX_KEY]; // keys
int values[MAX_DATA]; // values
Init Function
- Make
key-valuepairs using random function.
void init() {
// hash table initiation
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_TABLE; ++i) {
Node * cur = tb[i];
Node * tmp;
while (cur != NULL) {
tmp = cur;
cur = cur->next;
free(tmp);
}
tb[i] = NULL;
}
// srand and seed for random function
srand(time(NULL));
// init values
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_DATA; ++i) {
values[i] = rand() % 100 + 1;
}
// init keys
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_DATA; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < MAX_KEY - 1; ++j) {
keys[i][j] = rand() % 26 + 97; // ASCII 97 ~ 122
}
keys[i][MAX_KEY - 1] = '\0';
}
}
String Function
- Compare and copy function.
void my_str_cpy(char * dest, const char * src) {
while (*src != '\0') {
*dest = *src;
dest++; src++;
}
*dest = '\0';
}
int my_str_cmp(const char * str1, const char * str2) {
while (*str1 != '\0' && (*str1 == *str2)) {
str1++;
str2++;
}
return *str1 - *str2;
}
Hash Function
- Just use same function as above
- Use shift operatoin and prime number
- We need to divide it by
MAX_TABLEfor hash table array.
int hash(const char * str) {
int hash = 401;
int c;
while (*str != '\0') {
hash = ((hash << 4) + (int)(*str)) % MAX_TABLE;
str++;
}
return hash % MAX_TABLE;
}
Add
- Simpel linked list hash add implementation
- If there is same key in hash table, then replace its value.
void add(const char * key, int value) {
Node * new_node = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
my_str_cpy(new_node->key, key);
new_node->value = value;
new_node->next = NULL;
int index = hash(key);
// insert if first is NULL
if (tb[index] == NULL) {
tb[index] = new_node;
}
// traverse list one by one
// change duplicated value if not then add it to front
else {
Node * cur = tb[index];
while (cur != NULL) {
// if key is duplicated, then replace its value
if (my_str_cmp(cur->key, key) == 0) {
cur->value = value;
return;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
// add to front if it is not duplicated
new_node->next = tb[index];
tb[index] = new_node;
}
}
Find Value
- Use linked list for finding.
- If there is matching key, then save it to
valand returntrue. - If there is no matching key, then return
false
bool find(const char * key, int * val) {
int index = hash(key);
Node * cur = tb[index];
// Find key by traversing list one by one
while (cur != NULL) {
if (my_str_cmp(cur->key, key) == 0) {
*val = cur->value;
return true;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return false;
}
Deletion
- Delete node if key is matched.
- Just check the first of list. It makes easy for implementation.
bool destroy(const char * key) {
int index = hash(key);
// check first of list
if (tb[index] == NULL) {
return false;
}
// check first element
if (my_str_cmp(tb[index]->key, key) == 0) {
Node * first = tb[index];
tb[index] = tb[index]->next;
free(first);
return true;
}
// others
else {
Node * cur = tb[index]->next;
Node * prev = tb[index];
while (cur != NULL && my_str_cmp(cur->key, key) != 0) {
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
if (cur == NULL) return false;
prev->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
return true;
}
}
- Print all
key-valuepairs while traversing all table and lists.
void print_hash() {
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_TABLE; ++i) {
if (tb[i] != NULL) {
printf("index: %d\n", i);
Node * cur = tb[i];
while (cur != NULL) {
printf("{ %s, %d }, ", cur->key, cur->value);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
}
Main
- Test add, find and destroy functions.
int main() {
char tmp_key[MAX_KEY];
init();
// Add
printf("Add to hash table\n");
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_DATA; ++i) {
add(keys[i], values[i]);
}
print_hash();
printf("\n");
// Delete
printf("Deleted keys: ");
for (int i = 0; i < DELETE_COUNT; ++i) {
my_str_cpy(tmp_key, keys[rand() % MAX_DATA]);
printf("%s ", tmp_key);
destroy(tmp_key);
}
printf("\n");
print_hash();
printf("\n");
// Find
int val;
printf("Found: ");
for (int i = 0; i < FIND_COUNT; ++i) {
my_str_cpy(tmp_key, keys[rand() % MAX_DATA]);
if (find(tmp_key, &val)) {
printf("{ %s, %d } ", tmp_key, val);
}
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#define MAX_TABLE 5 // size of table
#define MAX_KEY 8 // include null
#define MAX_DATA 12 // num of datas for hash table
#define DELETE_COUNT 6 // num of datas for deletion
#define FIND_COUNT 8 // num of datas for finding
struct Node {
char key[MAX_KEY];
int value;
Node * next;
};
Node * tb[MAX_TABLE]; // hash table
char keys[MAX_DATA][MAX_KEY]; // keys
int values[MAX_DATA]; // values
void init() {
// hash table initiation
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_TABLE; ++i) {
Node * cur = tb[i];
Node * tmp;
while (cur != NULL) {
tmp = cur;
cur = cur->next;
free(tmp);
}
tb[i] = NULL;
}
// srand and seed for random function
srand(time(NULL));
// init values
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_DATA; ++i) {
values[i] = rand() % 100 + 1;
}
// init keys
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_DATA; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < MAX_KEY - 1; ++j) {
keys[i][j] = rand() % 26 + 97; // ASCII 97 ~ 122
}
keys[i][MAX_KEY - 1] = '\0';
}
}
void my_str_cpy(char * dest, const char * src) {
while (*src != '\0') {
*dest = *src;
dest++; src++;
}
*dest = '\0';
}
int my_str_cmp(const char * str1, const char * str2) {
while (*str1 != '\0' && (*str1 == *str2)) {
str1++;
str2++;
}
return *str1 - *str2;
}
int hash(const char * str) {
int hash = 401;
int c;
while (*str != '\0') {
hash = ((hash << 4) + (int)(*str)) % MAX_TABLE;
str++;
}
return hash % MAX_TABLE;
}
void add(const char * key, int value) {
Node * new_node = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
my_str_cpy(new_node->key, key);
new_node->value = value;
new_node->next = NULL;
int index = hash(key);
// insert if first is NULL
if (tb[index] == NULL) {
tb[index] = new_node;
}
// traverse list one by one
// change duplicated value if not then add it to front
else {
Node * cur = tb[index];
while (cur != NULL) {
// if key is duplicated, then replace its value
if (my_str_cmp(cur->key, key) == 0) {
cur->value = value;
return;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
// add to front if it is not duplicated
new_node->next = tb[index];
tb[index] = new_node;
}
}
bool find(const char * key, int * val) {
int index = hash(key);
Node * cur = tb[index];
// Find key by traversing list one by one
while (cur != NULL) {
if (my_str_cmp(cur->key, key) == 0) {
*val = cur->value;
return true;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return false;
}
bool destroy(const char * key) {
int index = hash(key);
// check first of list
if (tb[index] == NULL) {
return false;
}
// check first element
if (my_str_cmp(tb[index]->key, key) == 0) {
Node * first = tb[index];
tb[index] = tb[index]->next;
free(first);
return true;
}
// others
else {
Node * cur = tb[index]->next;
Node * prev = tb[index];
while (cur != NULL && my_str_cmp(cur->key, key) != 0) {
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
if (cur == NULL) return false;
prev->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
return true;
}
}
void print_hash() {
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_TABLE; ++i) {
if (tb[i] != NULL) {
printf("index: %d\n", i);
Node * cur = tb[i];
while (cur != NULL) {
printf("{ %s, %d }, ", cur->key, cur->value);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
}
int main() {
char tmp_key[MAX_KEY];
init();
// Add
printf("Add to hash table\n");
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_DATA; ++i) {
add(keys[i], values[i]);
}
print_hash();
printf("\n");
// Delete
printf("Deleted keys: ");
for (int i = 0; i < DELETE_COUNT; ++i) {
my_str_cpy(tmp_key, keys[rand() % MAX_DATA]);
printf("%s ", tmp_key);
destroy(tmp_key);
}
printf("\n");
print_hash();
printf("\n");
// Find
int val;
printf("Found: ");
for (int i = 0; i < FIND_COUNT; ++i) {
my_str_cpy(tmp_key, keys[rand() % MAX_DATA]);
if (find(tmp_key, &val)) {
printf("{ %s, %d } ", tmp_key, val);
}
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Verification
- Modify hash function name(hash->my_hash)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#define TOTAL_TEST_CASE 100
#define MAX_TABLE 300 // size of table
#define MAX_KEY 8 // include null
#define MAX_DATA 2000 // num of datas for hash table
#define DELETE_COUNT 1000 // num of datas for deletion
using namespace std;
struct Node {
char key[MAX_KEY];
int value;
Node * next;
};
Node * tb[MAX_TABLE]; // hash table
char keys[MAX_DATA][MAX_KEY]; // keys
int values[MAX_DATA]; // values
void init() {
// hash table initiation
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_TABLE; ++i) {
Node * cur = tb[i];
Node * tmp;
while (cur != NULL) {
tmp = cur;
cur = cur->next;
free(tmp);
}
tb[i] = NULL;
}
// srand and seed for random function
srand(time(NULL));
// init values
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_DATA; ++i) {
values[i] = rand() % 100 + 1;
}
// init keys
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_DATA; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < MAX_KEY - 1; ++j) {
keys[i][j] = rand() % 26 + 97; // ASCII 97 ~ 122
}
keys[i][MAX_KEY - 1] = '\0';
}
}
void my_str_cpy(char * dest, const char * src) {
while (*src != '\0') {
*dest = *src;
dest++; src++;
}
*dest = '\0';
}
int my_str_cmp(const char * str1, const char * str2) {
while (*str1 != '\0' && (*str1 == *str2)) {
str1++;
str2++;
}
return *str1 - *str2;
}
int my_hash(const char * str) {
int hash = 401;
while (*str != '\0') {
hash = ((hash << 4) + (int)(*str)) % MAX_TABLE;
str++;
}
return hash % MAX_TABLE;
}
void add(const char * key, int value) {
Node * new_node = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
my_str_cpy(new_node->key, key);
new_node->value = value;
new_node->next = NULL;
int index = my_hash(key);
// insert if first is NULL
if (tb[index] == NULL) {
tb[index] = new_node;
}
// traverse list one by one
// change duplicated value if not then add it to front
else {
Node * cur = tb[index];
while (cur != NULL) {
// if key is duplicated, then replace its value
if (my_str_cmp(cur->key, key) == 0) {
cur->value = value;
return;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
// add to front if it is not duplicated
new_node->next = tb[index];
tb[index] = new_node;
}
}
bool find(const char * key, int * val) {
int index = my_hash(key);
Node * cur = tb[index];
// Find key by traversing list one by one
while (cur != NULL) {
if (my_str_cmp(cur->key, key) == 0) {
*val = cur->value;
return true;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return false;
}
bool destroy(const char * key) {
int index = my_hash(key);
// check first of list
if (tb[index] == NULL) {
return false;
}
// check first element
if (my_str_cmp(tb[index]->key, key) == 0) {
Node * first = tb[index];
tb[index] = tb[index]->next;
free(first);
return true;
}
// others
else {
Node * cur = tb[index]->next;
Node * prev = tb[index];
while (cur != NULL && my_str_cmp(cur->key, key) != 0) {
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
if (cur == NULL) return false;
prev->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
return true;
}
}
void print_hash() {
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_TABLE; ++i) {
if (tb[i] != NULL) {
printf("index: %d\n", i);
Node * cur = tb[i];
while (cur != NULL) {
printf("{ %s, %d }, ", cur->key, cur->value);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
}
int main() {
int test_case = 1;
int correct = 0;
for (test_case = 1; test_case <= TOTAL_TEST_CASE; ++test_case) {
init();
bool is_equal = true;
map<string, int> m;
map<string, int>::iterator it;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_DATA; ++i) {
add(keys[i], values[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_DATA; ++i) {
if (m.count(keys[i]) == 0) {
m.insert(make_pair(keys[i], values[i]));
}
else {
m[keys[i]] = values[i];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_DATA; ++i) {
int tmp;
find(keys[i], &tmp);
if (m[keys[i]] != tmp) {
is_equal = false;
}
}
char tmp_key[MAX_KEY];
for (int i = 0; i < DELETE_COUNT; ++i) {
my_str_cpy(tmp_key, keys[rand() % MAX_DATA]);
destroy(tmp_key);
m.erase(tmp_key);
}
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_DATA; ++i) {
int tmp = -1;
if (find(keys[i], &tmp) == false && m.count(keys[i]) == 0) {
continue;
}
if (find(keys[i], &tmp) == true && m.count(keys[i]) == 1 && m[keys[i]] == tmp) {
continue;
}
else {
is_equal = false;
}
}
if (is_equal) correct++;
}
printf("Total: %d / %d\n", correct, TOTAL_TEST_CASE);
return 0;
}
