[Algorithm] C++에서 그래프 탐색(DFS와 BFS) 구현하기
업데이트(2020.07.12): GIF 이미지 변경
업데이트(2020.06.14): 배열의 크기를 변수로 받아서 동적으로 그래프를 생성하는 예시 추가
업데이트(2019.03.02): DFS, BFS 이미지 추가
업데이트(2018.04.07): Stack을 이용한 DFS 방식 추가
C++에서 그래프 탐색(DFS와 BFS)을 구현하는 방법을 알아보자.
환경 및 선수조건
- C++
- C++에서 그래프 구현하기
탐색
개념
- DFS(깊이우선탐색): 현재 정점에서 갈 수 있는 점들까지 들어가면서 탐색

- BFS(너비우선탐색): 현재 정점에 연결된 가까운 점들부터 탐색
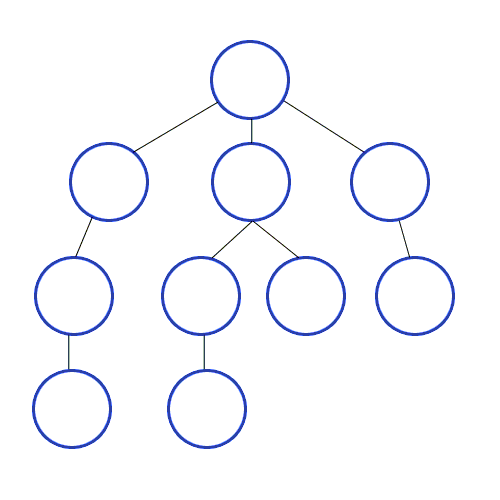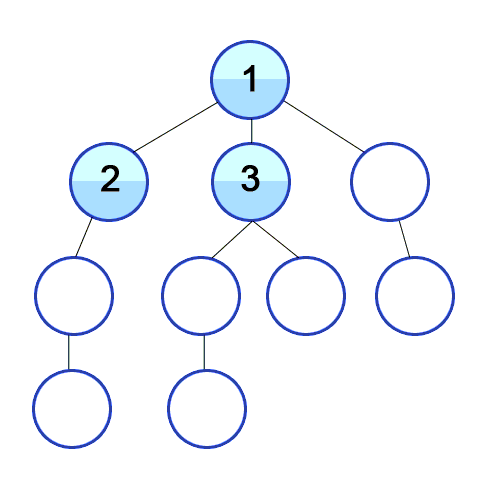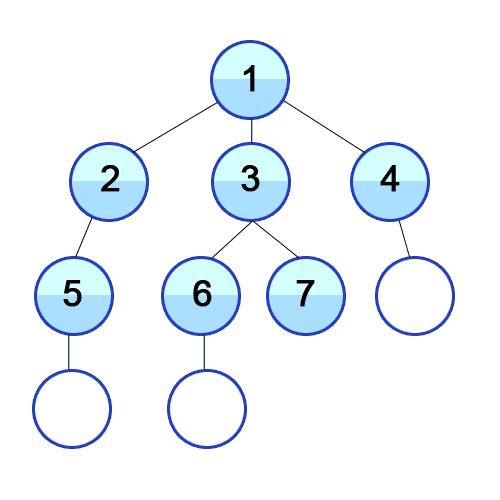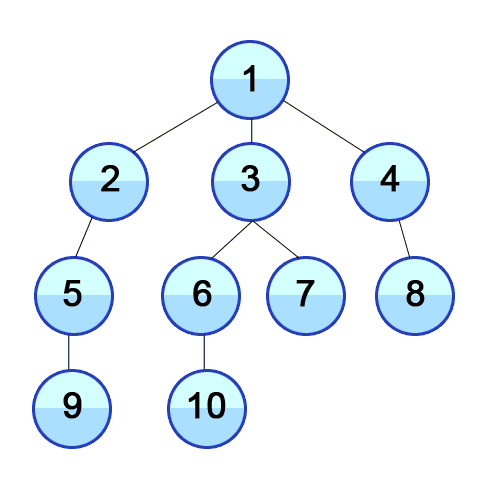
- 위의 이미지를 참고하시면 비교가 쉽습니다. 해당 번호 순서대로 탐색을 합니다.
방법
- DFS: 스택 또는 재귀함수로 구현
- BFS: 큐를 이용해서 구현
구현
- List(여기서는 vector)를 통해서 구현
- https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1260 풀이와 관련된 구현
- graph[]: List를 통해서 구현한 그래프
- check[]: 탐색을 했으면 true 아니면 false로 구분
DFS
Recursion 이용
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
// dfs에 들어오면 '방문'한거로 판단
// 해당 위치에 check true로 해준다.
void dfs(int start, vector<int> graph[], bool check[]){
check[start]= true;
printf("%d ", start);
for(int i=0; i < graph[start].size(); i++){
int next = graph[start][i];
// 방문하지 않았다면
if(check[next]==false){
// 재귀함수를 호출한다.
dfs(next, graph, check);
}
}
}
int main (){
int n, m, start;
cin >> n >> m >> start;
vector<int> graph[n+1];
// Visual Studio의 경우
/* 변수를 통해서 배열을 동적으로 생성할 때
vector<int> * graph = new vector<int>[n+1];
*/
bool check [n+1];
fill(check, check+n+1, false);
for(int i=0; i<m; i++){
int u,v;
cin >> u >> v;
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
// Sorting은 왜 한거지?
// 나중에 하나의 정점에서 다음을 탐색할 때 node 값에 순차적으로 접근해야하기 때문
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
sort(graph[i].begin(), graph[i].end());
}
//dfs
dfs(start, graph, check);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Stack 이용
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
// stack에 들어가면 방문한거로 판단
// 해당 위치를 true로 해준다.
void dfs(int start, vector<int> graph[], bool check[]){
stack<int> s;
s.push(start);
check[start] = true;
printf("%d ",start);
while(!s.empty()){
int current_node = s.top();
s.pop();
for(int i=0; i<graph[current_node].size(); i++){
int next_node = graph[current_node][i];
if(check[next_node]==false){
printf("%d ", next_node);
check[next_node] = true;
// pop()을 했었기 때문에 현재 current_node도 넣어줘야한다.
s.push(current_node);
s.push(next_node);
break;
}
}
}
}
int main (){
int n, m, start;
cin >> n >> m >> start;
vector<int> graph[n+1];
// Visual Studio의 경우
/* 변수를 통해서 배열을 동적으로 생성할 때
vector<int> * graph = new vector<int>[n+1];
*/
bool check [n+1];
fill(check, check+n+1, false);
for(int i=0; i<m; i++){
int u,v;
cin >> u >> v;
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
// Sorting은 왜 한거지?
// 나중에 하나의 정점에서 다음을 탐색할 때 node 값에 순차적으로 접근해야하기 때문
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
sort(graph[i].begin(), graph[i].end());
}
//dfs
dfs(start, graph, check);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
BFS
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
void bfs(int start, vector<int> graph[], bool check[]){
queue<int> q;
q.push(start);
check[start] = true;
while(!q.empty()){
int tmp = q.front();
q.pop();
printf("%d ",tmp);
for(int i=0; i<graph[tmp].size(); i++){
// 방문하지 않았다면
if(check[graph[tmp][i]] == false){
// 큐에 넣어주고 방문했음을 표시한다.
q.push(graph[tmp][i]);
check[graph[tmp][i]] = true;
}
}
}
}
int main (){
int n, m, start;
cin >> n >> m >> start;
vector<int> graph[n+1];
// Visual Studio의 경우
/* 변수를 통해서 배열을 동적으로 생성할 때
vector<int> * graph = new vector<int>[n+1];
*/
bool check [n+1];
fill(check, check+n+1, false);
for(int i=0; i<m; i++){
int u,v;
cin >> u >> v;
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
// Sorting은 왜 한거지?
// 나중에 하나의 정점에서 다음을 탐색할 때 node 값에 순차적으로 접근해야하기 때문
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
sort(graph[i].begin(), graph[i].end());
}
//bfs
bfs(start, graph, check);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
