컴퓨터 전공 11년 차, 블로그 6년 차 그리고 직장인으로서 5년 차 시작에 대한 회고
배경
어려서부터 과학과 공학 그리고 컴퓨터나 전자기기를 좋아했었고 원하는 대학에 입학해서 전공을 공부하기 시작한지 대략 10년이 넘었다. 올해를 포함해 간단하게 정리해보면 아래와 같다.
- 전공 공부를 시작한지 11년 차
- 기술블로그를 시작한지 6년 차
- 직장에 다니기 시작한지 5년 차
생각보다 많은 시간이 흘렀고 많은 일들과 경험 그리고 생각의 변화들이 있었다. 긍정일지 부정일지 이걸 남에게 공개해서 괜찮을지는 모르겠지만… 그래도 전공자, 블로거 그리고 직장인으로서의 회고를 한번에 정리해보면 좋을거 같아서 적어본다. 새해부터 바쁘고 해야할 일들이 많으니 핵심과 필요한 부분들만 적어볼까?!
전공자로서
꿈과 달려온 길
컴퓨터를 전공하여 열정적으로 공부하고 분야에서 활동한지 10년이 넘어간다. 앞서 기술했지만 어려서부터 전자기기나 과학이나 공학을 좋아했고 컴퓨터 관련해서도 잘 다뤄서 꿈을 IT쪽으로 잡았다. 위인전도 많이 읽었고 나라가 자랑스러워 나라를 빛낼 수 있는 사람이 되고 싶었다. 자라면서 스티브 잡스의 영상 그리고 신종균 사장님의 발표 영상들을 보면서 영감을 받았다. 나도 언젠가는 저 자리에서 발표를 하면서 이 나라와 회사를 든든하게 만들고 내 가족과 소중한 사람들을 지키는게 꿈이었다.
그래서 컴퓨터를 전공하였고 원하는 대학을 갔고 10년간 열정적으로 학교 공부도 충실히하고 이런저런 다양한 활동을 하면서 열심히 살아왔다.
10년간 즐겁게 그리고 열정적으로 일했던거 같다. 최근에서야 그 열정이 떨어졌지만… 그래도 최근을 제외하고는 이 분야만큼 재밌는게 없을정도로 좋아했다.
인생에서 중요한거
현재 다니는 회사에서 임원을 다는걸 목표로 열심히 했다. 남들이 어떤말을 하더라도 계속 방법을 찾아보고 열정적으로 했다. 임원이 되고자 했던 이유는 전공을 좋아하고 나라에 기여하고 그래야 가족과 주변을 지킬 수 있을거 같아서다.
그런데 최근에 회사를 다니고 주변을 돌아보면서 생각이 바뀌었다. 가족이 제일 중요한데 일에만 집중하느라 가족을 돌보지 못하는거 같았다. 강아지이자 동생이 있는데 눈이 하나 멀어가는것도 알아차리지 못하고(왼쪽눈은 정상이라 감사하다.) 가족이랑 보내는 시간을 소홀히한거 같았다. 단순히 이게 일때문이라고는 할 수 없지만 당연히! 이걸 느끼는 순간 나에게 가장 중요한건 가족과 주변 사람이라는걸 깨달았다.
그러면서 내 가족을 돌볼수 있는 일들을 조금 더 하고싶은 마음이 생겼고 그리하여 수의학이나 의학을 다시 공부하고 싶은 마음도 생겼다. 당연히 내 수능점수로는 갈 수 없었는데 다시 도전해보고 싶은 마음도 진지하게 있었고 수의대의 경우 지방까지 편입을 알아봤었다.
수의학을 전공하면 우리집 강아지를 직접 내가 돌볼 수 있고 가족이 아플때도 다르게 도와줄 수 있지 않을까?라는 생각이 들었었다.
추가적으로 어려서부터 나라를 지키거나 남들을 도와주고 싶었다. 수의학을 전공해서 정말 도움받지 못하는 동물들을 도와주는게 의미있어보였고 그렇게해서 직접적으로 돕고싶은 생각이 정말 많이 들었다. 매달 동물단체에 기부도 하고 있는데 어려운 상황에 있는 동물들을 보면 도와주고 싶었고 사람들이 사람들은 많이 돕지만 동물들은 돕지 않으니 더 도와주고 싶은 마음이 생겼다.
이전까지는 나라가 자랑스럽고 성장을 많이했지만 현재 내가 보는 우리나라는 걱정이 더 크다. 역피라미드 구조에 출산율은 바닥이고 부동산은 폭등했으며 여전히 사람들은 자기생각에 사로잡혀 실리를 추구하기보다 싸우기에만 바쁘기에 밝은 미래가 보이지 않는다. 그래서 나라의 미래가 밝기보다 어두워보이는데 나라를 위해서 뭘 하고싶다는 생각이 좀 줄어들었다. 이러한 부분은 제발 내 예상이 틀렸기를 바라며 다시 자랑스러운 나라가 되면 좋겠다.
결론적으로 생각해보면 내 인생에서 중요한건 가족과 내 주변 사람들이고 남들을 도와주는걸 하고 싶었던거 같다. 그런 중요한 부분과 함께 IT가 적성에 맞았다고 볼 수 있을거 같다.
그렇다면 지금은?
그렇다고 지금하고 있는일들이 싫다는건가?! 그건 아니다! 인생에서 중요한게 무엇인지 한번 더 확인하는 계기가 되었다. 하지만 여전히 IT분야가 재밌고 제일 적성에 맞긴하다. 수의학에 대해서 관심이 많이 추가된것이지 여전히 이 분야가 새롭고 재미있긴하다. 동물에 대한 관심이나 주식과 같은 새로운 관심사들도 생겼지만 여전히 이 분야가 재밌고 일로 하기에는 괜찮다. 이전보다 줄었지만 여전히 있다고 정리하면 될거 같다.
그래서 앞으로는 동물에 관련된 활동과 공부를 추가해서 병행해보는거로 목표를 잡았다. 비록 지금 다시 공부를 해서 수의학을 전공하기에는 무리지만… 다른 방식으로 어떻게 내가 배운거로 도울 수 있을지를 고민해보는중이다. 그 방법에는 봉사도 있고 기부도 있고 서비스 개발 등등 여러가지 방법이 있을거 같다.
주식이나 다른 관심사들도 꾸준하게 공부할 예정이며 일은 여전히 관심 있으니 일대로 하고 다른 부분들도 회사 밖에서 열심히 활동해볼 예정이다.
그리고 가장 중요한건 가족과 사람으로 가족과 주변 사람들과 시간 보내는걸 제일 중요하게 하고싶다.
갑자기 전공이 아닌 인생회고가 된거 같지만 그만큼 이 분야와 내 인생에 관련이 컸기때문에 위처럼 회고가 진행된거 같다.
블로거로서
지금까지
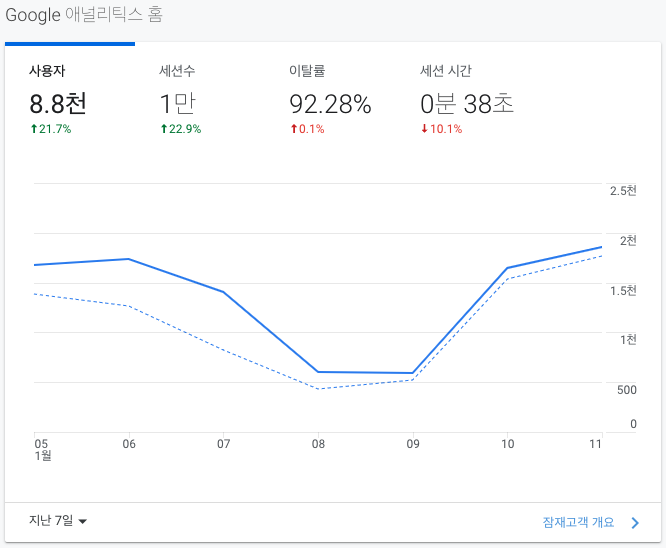

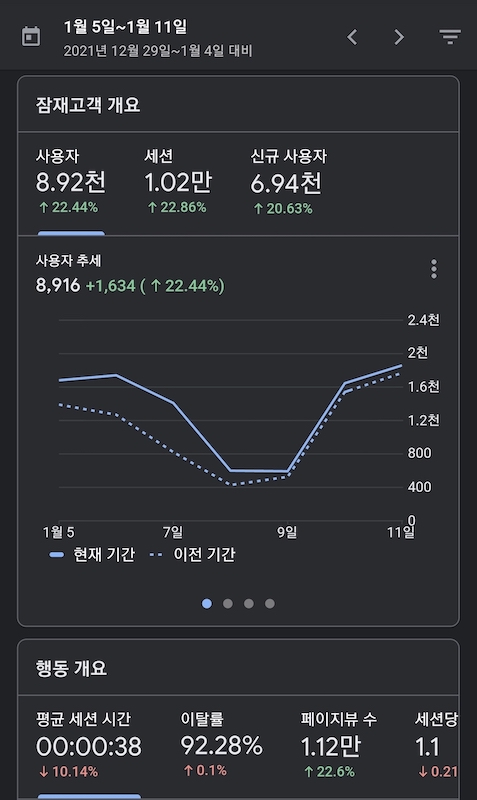
많은 사람들이 봐주시고 질문도 남겨주시고 있어서 뿌듯하다. 내가 공부한걸 정리하려고 만든 블로그지만 사람들이 들어오는건 언제나 좋다. Good!
작년의 목표들
우선 작년에 목표로 잡았던 부분들을 정리해보면 아래와 같다. [회고] 4년 차 기술 블로거의 블로그 운영 회고와 [회고] 2021년 2월의 짧은 회고 이렇게 2개의 회고가 있었었다.
- 내용에 집중하자
- 컴퓨터 언어를 언급할때는 소문자로 명시해야하는게 아니면 대문자를 사용하자
- 기존에 있는 문서들은 문제를 발견하면 그때 수정하자
- 내용 > 레이아웃과 형식
- 전문적인 내용의 글을 추가
- 기존과 같이 글을 쓰던 방식은 유지
“전문적인 내용의 글을 추가”를 제외하면 전체적으로 목표를 이룬거 같다. 간단한 내용일수 있지만 다른것보다 내용을 잘 정리하는거에 집중했었다.
“전문적인 내용의 글을 추가”의 경우 핑계를 대자면 회사 업무외에 전문적인 글을 볼 시간이 없었다. 가족과의 시간 보내기, 주식, 일상 블로그, 친구 만나기 등등 여러 일들을 하면서 전문적이기보다 지식이나 새로운걸 조사하는데 시간을 더 많이썼다. 즉, 전문적인거 하나 볼 시간에 다른 도움이 될만한 여러 지식들 3~4개를 썼다고 볼 수 있다.
“컴퓨터 언어를 언급할때는 소문자로 명시해야하는게 아니면 대문자를 사용하자” 이 부분을 지금보니 지금은 전혀 그렇지 않는데 저걸 작성할 당시에는 약간 글 작성에 너무 완벽과 통일성을 중시했던거 아닌가 싶다. 지금보면 왜그랬나 싶다ㅋㅋ
올해와 앞으로는?
블로그는 여전히 재밌고 나한테 있는 여러 좋은 작품들중 하나이다. 기록하는게 재밌고 사람들이 들어오고 소통하는거 그리고 포트폴리오의 일부분으로 쓸 수 있는게 큰 장점이다. 공부하다가 생각난거 아니면 일하다가 회사와 관련없이 정리할 수 있는 부분들을 정리하는건 재밌고 유익하다.
앞으로 또 변경될 수 있지만 올해와 앞으로의 목표는 아래와 같다.
- 쓰고싶은 내용들을 정리하자
무겁게 전문적인 글 10개를 쓰자거나 어떤 내용들을 몇개 채우겠다는 이런 목표보다는 현재처럼 공부하다가 필요한 내용을 정리하거나 공유하면 좋을 내용들을 적어나가려한다.
직장인으로서
어려서부터 원하던 회사에 입사
어려서부터 지금 회사 제품들을 사용했었고 꿈에 그리던 회사에 들어왔다. 앞서 서술한대로 내가 좋아하는 분야에서 세계를 대상으로 경험과 실력을 쌓으려면 여기만한곳이 없다고 생각했다. 실제로 지금도 여기가 제일 목표한 방향에 가까운 회사이긴하다. 이제 회사에 다닌지는 5년 차에 접어들었다.
원하던 회사에 들어왔지만 현재는 좀 조심스럽긴한데… 예전같은 마음은 아닌거 같다. 회사에 관련된 내용이 있을 수 있어서 자세한 내용들을 적기는 어렵지만 더 경험과 실력을 쌓을 수 있는 큰 회사로 가고싶은 마음도 있다.
다시 정리하면 초등학생때부터 원하던 회사에 들어왔고 현재는 5년 차이며 입사까지는 꿈을 이룬 상태였다. 현재 어느정도 만족은 하지만 더 좋은 회사 이직에 관한 부분도 열려있다.
현재 회사
하고 싶은 말들이 좀 있지만 공개된 장소이고 회사에서 날 어떻게 할지도 모르니 말을 조심해야겠다… 그래도 종합적으로 봤을때는 나쁘지 않다. 다만, 여기서 안주하면 안될거 같고 끊임없이 따로 공부하고 살 방법을 모색해야할거 같다. 일만 집중해서는 한계가 있어보인다.
커리어
커리어가 조금 생각한거보다 다르게 쌓이긴했다. 처음에는 클라우드쪽의 일을 하고 싶었는데 1년반정도는 관련 일을 했고 1년은 로깅 관련 그리고 나머지 1년은 데이터 수집 관련된 일을 했다. 5년 차이지만 정확하게는 3년 7개월째 근무중이다.
하나를 좀 깊게 해보고 싶은데 그러지 못해서 현재 커리어가 조금 꼬여있긴하다. 하나를 오래해야 이직하거나 할때 조금 더 필요한 인력이 될 수 있는데 그러지 못한부분이 아쉽다.
다행인건 올해도 작년과 같은 일을해서 그래도 커리어를 이쪽으로는 조금 더 쌓을 수 있을거 같다.
하고 싶은 부분들은 여전히 클라우드, 플랫폼 그리고 데이터쪽인데 완전히는 아니지만 그래도 관련된 일들을 비슷하게 해온거 같다.
앞으로도 커리어가 걱정이다. 그래도 현재 하고있는 데이터 수집과 적재 관련해서 2년정도는 더 쌓고싶다.
앞으로
앞서 서술한대로 커리어가 걱정이긴하다. 수시로 업무가 바뀐 상황을 겪어서 미래가 걱정이다. 그래도 회사에 내 인생을 맡길 수 없으니 스스로 따로 클라우드, 플랫폼 그리고 데이터 관련 공부도 하고 회사와 병행해서 내 앞길을 찾을 방향을 계속 모색하는중이다.
커리어와 별개로 회사원들의 직장 수명은 한국 기준 보수적으로 잡을때 40대 중반으로 보인다(이건 데이터에 근거하기보다 내가 다니는 회사와 부서에 40대 중반 이상을 거의 찾아보기 힘들어서 내린 결론이다). 오래 잘 버티면 40대 중반까지인데 100세시대인 세상에 앞으로 어떻게 살아야할지가 걱정이다. 이래서 공부를 더하더라도 전문직을 했어야하나 싶기도하다. 이전까지는 노후보다는 현재와 공부에 집중했는데 보수적으로 계획을 잡아서 앞으로 40대 이후에는 어떻게 할지를 이제 구체적으로 계획을 잡아야할거 같다.
걱정
약 20년정도 안에 은퇴를 하는 상황이 올수도 있는데 그에 대한 대비도 조금씩 해야할거 같다. 수명은 점점 길어지는데 대기업에서의 수명은 여전히 짧으니까… 이러한 부분들이 조금씩 걱정인거 같다. 그래도 방법을 찾아야한다!
직장의 의미
직장은 내 꿈을 펼치는 곳이 아니고 내가 하고싶은 것만 하는곳이기는 힘들다. 철저히 회사와 다니는 사람은 계약 관계이다. 회사는 필요로 하는 일이 있으면 그러한 일을 할 수 있는 사람에게 돈을 주고 고용한거고 직장인은 그러한 일을 하기로 계약하여 들어간 사람이라 생각한다.
물론 여기서 오해의 소지가 있을 수 있는데 들어가서 회사의 근무 환경에 따라 하고 싶은 일들을 선택하고 자유롭게 의사를 표현하는건 전체적인 업무 효율과 환경에 있어서 매우 중요하다. 고용 관계이니 회사에 따라야한다를 말하는게 아니라 구조상 원하는 일들만 하기는 쉽지 않은 곳이라는거다. 그렇기에 회사와 나 사이에서 적정한 조율이 필요하다고 생각한다.
내가 회사에서 얻고자 하는것을 어떻게 얻을지 생각하면서 회사가 나에게 요구한것을 어떻게 달성할지를 생각해야하는거 같다. 그 두가지가 조화가 잘되면 최선이고 그게 아니라 너무도 다르면 부서를 이동하던가 다른 회사를 찾는것도 방법이다.
회사안에서 최대한 내 방향을 이루는 방식으로 생각해야하는거 같다. 역으로 이 회사에 다니면서 내가 살고자 그리고 하고자 하는 방향을 위해 회사를 어떻게 써먹을 수 있을지를 끊임없이 고민해야하는거 같다.
회사와 나는 계약 관계이기도 하지만 내가 사용할 수 있는 수단이기도 하다.
마무리
작성하고 의식의 흐름대로 작성하다 보니 의도와는 다르게 인생회고가 추가된거 같다.
수명을 100세라고 하면 약 인생의 1/3정도를 살았으며 직장의 경우 보수적으로 잡아 40대 중반에 일반적인 기업에서 퇴직을 한다고 가정했을때 1/4를 보냈다. 블로그의 경우 평생 작성할거고 IT의 경우도 평생이기에 끝나는 시점을 고려하고 있지 않다.
회고를 작성하면서 인생에서 중요한게 무엇인지 다시한번 정리했고 그걸 위해 내가 어떻게 해야할지 그리고 어떻게 살아야할지를 생각해보는 시간이 되었던거 같다.
30살까지 살다보니까 살다보면 종종 기회가 오는거 같다고 생각한다. 그 기회는 여러가지인데 시험, 주식, 비트코인, 연애, 부동산, 회사 등등 여러가지가 있을 수 있다. 나에게도 여러 기회가 나와 내 주변으로 생겼던거 같다(잡은것도 있고 못잡은것도 있다). 앞으로도 분명 기회는 올텐데 어느 순간에 올지 모르니 항상 스스로가 준비하고 있어야하는거 같다.
점점 더 바빠져서 앞으로 회고쓸 시간이 있을지 모르겠지만 그래도 내 인생 열심히 응원하면서 살아야겠다!
